Wikipedia suggests:
Src (gene)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| This article needs attention from an expert on the subject. (March 2011) |
| V-src sarcoma (Schmidt-Ruppin A-2) viral oncogene homolog (avian) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 PDB rendering based on 1a07. |
|||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbols | SRC; ASV; SRC1; c-SRC; p60-Src | ||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 190090 MGI: 98397 HomoloGene: 21120 ChEMBL: 267 GeneCards: SRC Gene | ||||||||||
| EC number | 2.7.10.2 | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||
| Entrez | 6714 | 20779 | |||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000197122 | ENSMUSG00000027646 | |||||||||
| UniProt | P12931 | P05480 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_005417.3 | NM_001025395.2 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_005408.1 | NP_001020566.1 | |||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 20: 35.97 – 36.03 Mb |
Chr 2: 157.42 – 157.47 Mb |
|||||||||
| PubMed search | [1] | [2 | |||||||||
Src (pronounced "sarc" as it is short for sarcoma) is a proto-oncogene encoding a tyrosine kinase originally discovered by J. Michael Bishop and Harold E. Varmus, for which they were awarded the 1989 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.[2] It belongs to a family of non-receptor tyrosine kinases called Src family kinases. The discovery of Src family proteins has been instrumental to the modern understanding of cancer as a disease where normally healthy cellular signalling has gone awry.
This gene is similar to the v-src gene of Rous sarcoma virus. This proto-oncogene may play a role in the regulation of embryonic development and cell growth. The protein encoded by this gene is a tyrosine-protein kinase whose activity can be inhibited by phosphorylation by c-SRC kinase. Mutations in this gene could be involved in the malignant progression of colon cancer. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene.[3]
==============================================================
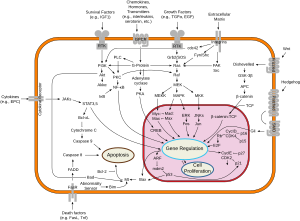
In fact, SRC gene is at the center of Metastatic process through interaction with cell adhesion molecules, growth factors and many signal transduction pathways:
Wikipedia:
Interactions
Src (gene) has been shown to interact with
- AR,[19][20][21]
- ARNT,[22]
- AHR,[22]
- ADRBK1,[23]
- ADRB3,[24]
- BCAR1,[25][26][27][28][29][30]
- CD44,[31]
- DAB2,[32]
- DDEF1,[33]
- DAG1,[34]
- EPHB2,[35][36]
- EGFR,[37][38][39]
- EPS8,[40]
- ESR1,[19][41][42][43]
- ESR2,[19][43]
- GNB2L1,[44]
- GRB2,[23][45]
- GRIN2A,[46][47]
- HNF1A,[48]
- KHDRBS1,[49][50][51][52][53]
- MT-ND2,[54]
- MUC1,[55][56]
- NCOA6,[57][58][59][60]
- PDE6G,[23]
- PLD2,[61]
- PRKCZ,[62]
- PTK2,[26][30][63][64][65][66]
- PTK2B,[38][67][68]
- RAF1,[69]
- RASA1,[70][71]
- RARA,[42][72]
- RICS,[73]
- SRF,[74]
- SHB,[75]
- STAT1,[37][76]
- STAT3,[77] and
- WAS.[78][79]
See also
Genatlas:- c-SRC is non receptor tyrosine kinase, direct effector of G proteins
- c-SRC plays a role in the regulation of embryonic development and cell growth
- c-SRC has an appreciable role in the organization of the Golgi apparatus, which may be linked to its involvement in protein transport from the Golgi apparatus to the endoplasmic reticulum
- c-SRC has an appreciable role in the organization of the Golgi apparatus, which may be linked to its involvement in protein transport from the Golgi apparatus to the endoplasmic reticulum
- monopalmitoylated SFK required for VEGF mitogenic signaling with SRC and FYN, but maintaining distinct properties in the regulation of VEGF-mediated endothelial cell events (Pubmed 16400523)
- c-SRC regulates Golgi structure and KDELR1-dependent retrograde transport to the endoplasmic reticulum
- c-SRC has a key role in the maintenance of epithelial integrity (Pubmed 18305002)
- c-SRC is crucially involved in the ghrelin-mediated Akt activation (Pubmed 19262695)
- non palmitoylated SFK (Src-family tyrosine kinase), rapidly exchanged between the plasma membrane and late endosomes/lysosomes (suggest that SFK trafficking is specified by the palmitoylation state in the SH4 domain) (Pubmed 19258394)
- major kinase implicated in PTK2 phosphorylation, and is directly translocated from focal adhesions to membrane ruffles, thereby promoting formation of new adhesion complexes (Pubmed 19066724)
- interacting with PDLIM4 and PTPN13 (PDLIM4 suppresses SRC activation through interacting with SRC and PTPN13, allowing PTPN13-dependent dephosphorylation of SRC at the activation loop) (Pubmed 19307596)
- c-SRC inhibits SGK1-mediated phosphorylation hereby restoring the WNK4-mediated inhibition of ROMK channels thus suppressing K secretion) (Pubmed 19706464)
- c-SRC binds DVL2, a key phosphoprotein in Wnt signaling, at two positions: an SH3-binding domain and a C-terminal domain (Pubmed 19920076)
- ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- THIS SRC IS PIVOTAL AND CENTER TO ALL ACTIVITY INVOLVING THE SPREAD AND MAINTENANCE OF CANCER. IT IS SOMEWHAT CELL AND SPECIES SPECIFIC.
- WE PURPOSELY LEFT THE DASATINIB REFERENCE HERE TO INDICATE THAT SCIENTIST ARE TRYING TO TARGET THIS CROSS ROAD MOLECULAR STRUCTURE.
- IT'S ACTIVITY AT THE MET PROTEIN INSURE CANCER GROWTH AND VASCULARIZATION THROUGH MET EFFECT ON ANGIOGENESIS.
- REMEMBER MET DISTURBANCES ARE PROMINENT IN PAPILLARY RENAL CELL CANCER.
MET ACTIVITY INDUCED BY SRC ACTIVATION BY PHOSPHORYLATION SEEMS TO BE DETERMINED BY THE TYPE OF GROWTH FACTOR INDUCED. THROUGH HGFR, IT LEADS TO EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT IN THE EARLY CELL, AND TO WOUND HEALING IN RELEVANT TISSUE (SKIN), AND THROUGH HGF, IT LEADS TO MESENCHYMAL DIFFERENTIATION.
THROUGH MET, SRC LEADS TO RAS, PI3K/MAP K AND STAT EFFECTS
PHENOMENA AT THE MEMBRANE, A TRUE HISTORY, STILL UNFOLDING.
PLEASE ALSO NOTE CONFORMATION RAPPROCHEMENT BETWEEN SRC AND THE C-ABL WHERE IMITIMAB /GLEEVEC ACTS! SRC, CENTER OF METASTASIS, IS AN INTRODUCTION TO OUR FUTURE DISCUSSIONS.