DAPK1
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Death-associated protein kinase 1 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 PDB rendering based on 1ig1. |
|||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbols | DAPK1; DAPK | ||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 600831 MGI: 1916885 HomoloGene: 3626 ChEMBL: 2558 GeneCards: DAPK1 Gene | ||||||||||
| EC number | 2.7.11.1 | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||
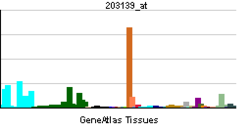 |
|||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||
| Entrez | 1612 | 69635 | |||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000196730 | ENSMUSG00000021559 | |||||||||
| UniProt | P53355 | Q80YE7 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_004938 | NM_029653 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_004929 | NP_083929 | |||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 9: 90.11 – 90.32 Mb |
Chr 13: 60.6 – 60.76 Mb |
|||||||||
| PubMed search | [1] | [2] | |||||||||
Death-associated protein kinase 1 is a positive mediator of gamma-interferon induced programmed cell death. DAPK1 encodes a structurally unique 160-kD calmodulin dependent serine-threonine kinase that carries 8 ankyrin repeats and 2 putative P-loop consensus sites. It is a tumor suppressor candidate.[2]
In melanocytic cells DAPK1 gene expression may be regulated by MITF.[3]"
AND YOU KNOW THAT ANYONE WHO WANTS TO LIVE WILL SILENCE THIS GENE. KILLING INTERFERON EFFECT IN LUNG CANCER DESPITE STRESS INDUCTION ROLE IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF LUNG CANCERS.
-------------------------------------------------------------------THIS GENE WAS DISCUSSED IN OTHER BLOG NOTE---------
2. GSTP1
GSTP1
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Glutathione S-transferase pi 1 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 PDB rendering based on 10gs. |
|||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbols | GSTP1; DFN7; FAEES3; GST3; GSTP; PI | ||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 134660 MGI: 95864 HomoloGene: 660 ChEMBL: 3902 GeneCards: GSTP1 Gene | ||||||||||
| EC number | 2.5.1.18 | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||
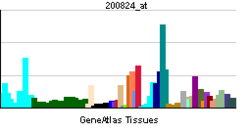 |
|||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||
| Entrez | 2950 | 14869 | |||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000084207 | ENSMUSG00000038155 | |||||||||
| UniProt | P09211 | P46425 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_000852 | NM_181796 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_000843 | NP_861461 | |||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 11: 67.35 – 67.35 Mb |
Chr 19: 4.04 – 4.04 Mb |
|||||||||
| PubMed search | [1] | [2] | |||||||||
Glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) are a family of enzymes that play an important role in detoxification by catalyzing the conjugation of many hydrophobic and electrophilic compounds with reduced glutathione. Based on their biochemical, immunologic, and structural properties, the soluble GSTs are categorized into 4 main classes: alpha, mu, pi, and theta. The glutathione S-transferase pi gene (GSTP1) is a polymorphic gene encoding active, functionally different GSTP1 variant proteins that are thought to function in xenobiotic metabolism and play a role in susceptibility to cancer, and other diseases.[3]
GSTP1 has been shown to interact with Fanconi anemia, complementation group C[4][5] and MAPK8.[6]"
METHYLATION HERE IS TO PERPETUATE THE ACTION OF CAUSING FACTORS. IT IS BAD FOR PATIENTS TO CONTINUE SMOKING ON TREATMENT. THIS IS AN EARLY EVENT IN TUMOR NEOPLASIA TRANSFORMATION.
Cyclic AMP mediated GSTP1 gene activation in tumor cells involves the interaction of activated CREB-1 with the GSTP1 CRE: a novel mechanism of cellular GSTP1 gene regulation.
PUTING THE EFFECT DEEP INTO THE MITOCHNDRIA. WHERE THE MTOR INHIBITORS WORK?
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 3.RAR BETA:This gene encodes retinoic acid receptor beta, a member
of the thyroid-steroid hormone receptor superfamily of nuclear |
4.ECAD
5.p14 ARF
6.p16
7.TIMP1
8.FHIT